Navigating the 3D Properties Dialog
The 3D Properties dialog is used when you want to change the size, location of the piece, physical attributes of fabric, etc. in order to affect the 3D simulation.
The 3D Properties dialog is dynamic according to what you have selected in the pattern. If you have selected a piece, the piece's properties appear, or if you have selected a stitch, the stitch's properties appear. For more information about Stitch properties, see Navigating the 3D Stitches Dialog.
To navigate the 3D Properties dialog:
Open PDS.
From the main menu
go to View > 3D Windows > 3D Properties.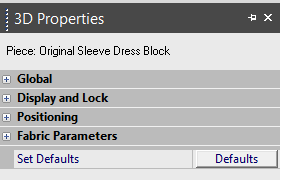
The 3D Properties are divided into the following categories.
Click to expand a category.
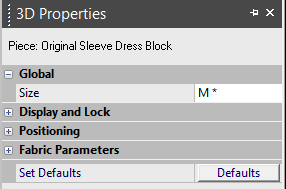
-
Size: Allows you to change the size of the garment. The sizes are calculated according to the Sizes Table in 2D. To change the size, select the size you require from the drop-down list. For example, select L. The size of the garment changes and the new size is displayed in the 3D window as follows:

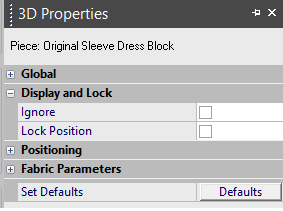
-
Ignore: Select this checkbox if you want certain pieces to be disregarded from the 3D window. For example, if you do not want the sleeves to be included when simulating.
-
Lock Position: Select this checkbox, if you want to the piece to be locked during simulation.
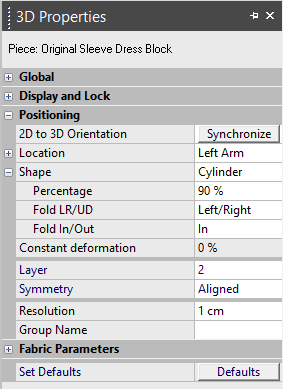
-
2D to 3D Orientation: Click the Synchronize button when you want make changes in 2D and you want it to take effect in 3D. For example, if a piece has been rotated in the Working Area.
-
Location: Displays the location of the piece in the 3D viewer. For example, if you want the piece to be defined as the front piece, select Front from the drop-down list. The list is pre-defined with the following location types:
-
-
Front: Place the piece flat in front of the model.
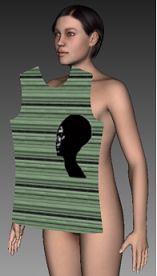
-
Back: Place flat at the model's back.

-
-
Left/Right: Place flat at the sides accordingly.
-
Top: Place flat approximately above the model's shoulders.

-
Bottom: Place flat approximately at the knee's height.

-
Left/Right Arm: Place as a 100% cylinder shape near the relevant arm.
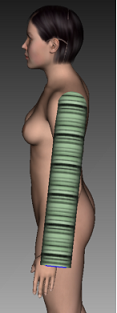
-
Left/Right Arm Low: Place as a 50% cylinder shape at the inner side of the arm.
-
Collar Stand: Locate a piece as 100% cylinder shape and place it approximately around the model's neck.

-
Collar Folded: Locate as a standard collar with 80% cylinder shape and place it approximately around the model's neck.

-
Add Custom Location: Click Create to create a customized location.
-
Save Custom as Current: Click Save to save the custom location so you can use it again.
-
Shape: Select a 3D shape for the 2D piece. This is to ensure the simulation is correct according to the 3D shape. The following shapes are available:
-
-
Flat: Displays the piece in the 3D window in a spread out manner, just like it looks on the Working Area.

-
Folded: Creates a 90 degrees fold in both ends of the piece.
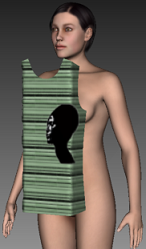
-
Cylinder: Bends the piece according to the percentage given by the user.
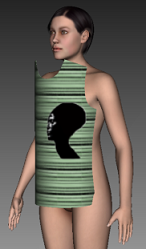
Note: The Shape fields are displayed according to the shape you have selected; therefore not all fields will be available.
-
-
Percentage: Bends the shape to the specified percentage.
-
Fold LR/UD: Bends the shape either in a Left Right direction, or Up Down.
-
Fold In/Out: Folds the shape In (the face turns out) or Out (face turns in).
-
Constant Deformation: Allows you to maintain the pre-simulation piece shape during simulation, according to its fabric bending.
-
Layer: Arranges the pieces in layers. Layer 1 is the lowest and closest to the body.
-
Symmetry: Defines the hierarchy of a single layer for paired pieces. You should use Symmetry only in cases where there's a piece which is defined as a pair or as a half piece and one piece or half overlaps the other. The default attribute is 'Aligned'. Change to 'Below' or 'Above' according to the orientation of the piece as it appears on the Working Area. In other words, if the orientation of the piece shown on the Working Area is left, and you know that the left side of the front should be below the right side of the front, then define the front piece as 'Below'.
-
Resolution: Each piece of cloth is represented in the 3D viewer by a mesh made of triangles. Smaller triangles means more accuracy to represent the piece's complex curved lines, folds and wrinkles.
-
-
Low resolution means bigger triangles to represent the piece and thus less accuracy in representing complex curved lines.

-
High resolution means smaller triangles to represent the piece and thus more accuracy in representing complex curved lines, folds and wrinkles..

Note: -
-
In most cases low resolution of 1.5 is enough to produce high quality simulation results.
-
Using high resolution cloth panels severely effects simulation performance (speed), so use this control wisely. Small pieces or pieces that should reveal folded details should have a low resolution value whereas large, generally flat pieces need not be simulated with thousands of triangles (in other words- high resolution values).
-
When simulating large pieces, set the resolution to be lower (value of 2-10).
-
-
-
Group Name: A common name for several pieces of one 3D group.
-
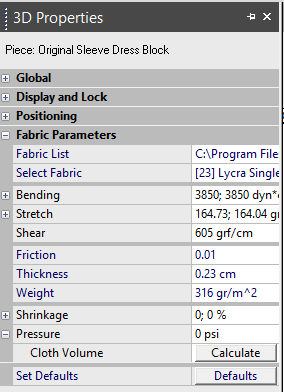
Fabric List: Click Browse to define the location of your fabric list. This list is provided by Optitex and contains a pre-defined list of different fabric types.
-
Select Fabric: Select a fabric from the drop-down list so you can modify its parameters.
-
Bending: Defines the resistance of the cloth to Bending forces. This important parameter effects the rigidity versus fluidity of the fabric. The higher the bending value - the stiffer the fabric. Low bending value - fluid fabric.
-
X: The X bending value.
-
Y: The Y bending value.
-
Stretch: The resistance of the cloth to Stretching forces in the Warp (X) and Woof (Y) directions. The parameters affect the elasticity of the fabric.
-
-
High value means high resistance to stretch force and thus - less elasticity.

-
Low value means low resistance to stretch force and thus- increased elasticity.

-
-
Shear: The resistance of the cloth to Shearing forces. Shearing forces influence is on the diagonal direction of the fiber/cloth or in other words, the parameter affects the gliding quality versus stiffness of a fabric.
-
-
High value means high resistance to shearing force and thus - less softness.

-
Low value means low resistance to shearing forces and thus - more softness and more accentuated body features.

-
-
Friction: The resistance of the cloth to its motion on the body's surface. The Friction parameter affects the way the cloth slides on the body.
-
-
High value means high resistance to motion on the body and therefor - the fabric will slide less on the body.

-
Low value means low resistance to motion on the body and therefor - the fabric will slide more on the body.

-
-
Thickness: The thickness of the fabric in CM.
-
-
Thin: Here is an example of a thin fabric set at 0.1 cm.

-
Thick: Here is an example of a thick fabric set at 0.5 cm.

-
-
Weight: The weight of the fabric in grams per square
-
-
High: Here is an example of a high fabric weight set at 250 gr.

-
Low: Here is an example of a low fabric weight, set at 50 gr.

-
-
Shrinkage: Some fabrics may shrink in the Warp and/or Woof directions as a result of chemical reactions that can occur during washing, drying, ironing etc. Use the Shrinkage factor to scale the garment (or part of it) to match its true size after shrinkage.
-
-
None:

-
5% shrinkage:

Note: The X and Y directions refer to directions on screen and not to the warp and woof of the fabric.
-
-
Pressure: Sets the artificial air pressure of the fabric.
-
Cloth Volume: Allows you to calculate the volume of the cloth of a 3D shape. Select the piece and then click Calculate.
-
Set Defaults: Click to return all values the default fabric values.
-
Puffy: If you need to produce puffiness, for example for winter coats, select this checkbox to define the piece as puffy.